PARTICIPATING LABS
Constam, Daniel
Multiple cancer hallmarks, including sustained proliferation, tumor angiogenesis, invasiveness and metastasis depend on cytokines of the Transforming Growth Factor β family (TGFβ). De-regulation of the balance between oncogenic and tumor-suppressive activities of these secreted factors, likely coupled to alterations in their signaling range, represents an important step in tumorigenesis and tumor evolution.
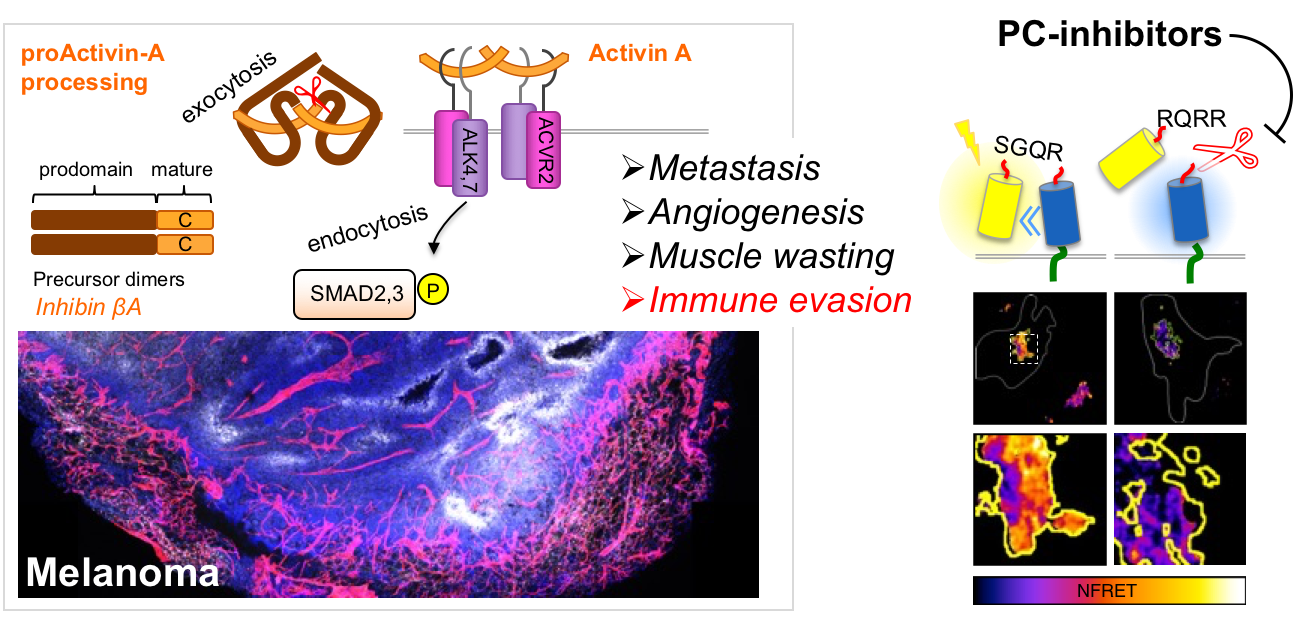
Certain TGFβ-related growth factors such as Activin-A are also released into the circulation as hormones, and/or to promote systemic muscle wasting during ageing. Similar systemic muscle wasting also accounts for up to 50% of cancer mortality in cancer. Furthermore, we recently found that abnormal expression and secretion of Activin-A can also promote tumor growth and metastasis in mouse models of melanoma, and that it does so by suppressing adaptive anti-tumor immunity (Donovan et al., 2017).
In order to stimulate its cell surface receptors, Activin-A must first mature from a secreted precursor dimer of two INHβA chains. However, a therapeutic strategy to block this process in human melanoma or in any other cancer type that frequently express INHβA is elusive (Ginefra et al., 2018).
Our current efforts therefore concentrate on elucidating how tumor cells and their microenvironment regulate the proteolytic maturation and secretion of Activin-A, and how this process or specific immunosuppressive signals downstream could be targeted to inhibit its oncogenic functions and/or restore tumor-suppressive activity.
Ongoing EICSE collaborations
- Single cell imaging of Activin secretion (Hatice Altug lab)
Key technologies
- Transgenic mouse models
- Multicolor flow cytometry
- FRET biosensors
- Proteomics & protein biochemistry
- Yeast-two-hybrid assay
Key biological questions
- Regulation of cancer hallmarks by TGFβ signaling
- Strategies to modulate TGFβ signaling outputs
- Proprotein convertases in development and disease and their spatial compartmentalization
- Targeted delivery of protease inhibitors





